What Are the Steps of ICSI
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is an advanced fertility treatment used in cases of male infertility. The process begins with ovarian stimulation, where hormonal medications help the female partner produce multiple eggs. These eggs are then retrieved through a minor surgical procedure. Meanwhile, sperm is collected and processed to select the healthiest one. A single sperm is injected directly into an egg under a microscope to enhance fertilization. The resulting embryos are cultured for a few days before the best-quality embryo is transferred into the uterus. After 12-14 days, a pregnancy test confirms the success of the procedure. Consulting an infertility specialist in Lahore can help determine if ICSI is the right option for you.
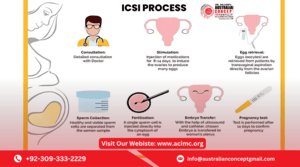
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is a specialized fertility treatment used in conjunction with In Vitro Fertilization (IVF). It is primarily recommended for couples experiencing male infertility issues, such as low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or abnormal sperm shape. Unlike conventional IVF, where sperm fertilizes the egg in a petri dish, ICSI involves injecting a single healthy sperm directly into an egg to increase the chances of fertilization.
Step 1: Ovarian Stimulation
The ICSI process begins with ovarian stimulation, where the female partner receives hormonal injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. The medications typically include:
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) to promote egg development.
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to trigger final egg maturation before retrieval.
During this phase, regular ultrasounds and blood tests monitor follicle growth to determine the best time for egg retrieval.
Step 2: Egg Retrieval (Oocyte Retrieval)
Once the eggs reach the desired maturity, they are retrieved through a minor surgical procedure called follicular aspiration. This process involves:
- Inserting a thin needle through the vaginal wall into the ovaries, guided by ultrasound.
- Extracting the eggs from the follicles using gentle suction.
- Collecting the eggs in a specialized laboratory for evaluation.
The procedure is performed under light sedation or anesthesia, making it painless for the patient.
Step 3: Sperm Collection and Preparation
On the same day as the egg retrieval, the male partner provides a semen sample, which is processed in the laboratory to select the best-quality sperm. If natural sperm collection is not possible due to azoospermia (absence of sperm in semen), sperm can be extracted surgically through Testicular Sperm Aspiration (TESA) or Micro-TESE.
During sperm preparation, embryologists:
- Wash and separate healthy, motile sperm from the seminal fluid.
- Use specialized techniques like motility assessment and morphology evaluation to select the best sperm for fertilization.
Step 4: Sperm Injection into the Egg
The most crucial step in ICSI is the intracytoplasmic injection itself. This is performed under a high-powered microscope, where an embryologist:
- Holds the mature egg with a specialized holding pipette.
- Selects a single healthy sperm using a fine glass needle.
- Injects the sperm directly into the egg’s cytoplasm.
- Places the fertilized eggs in a culture medium for incubation.
This precise process bypasses natural fertilization barriers and significantly improves the chances of fertilization, especially in cases of severe male infertility.
Step 5: Embryo Culture and Development
After fertilization, the embryos are closely monitored in a laboratory for 3 to 5 days to assess their quality. The embryologist checks for proper cell division and selects the most viable embryo(s) for transfer.
- On Day 3, embryos typically have 6-8 cells and are assessed for growth.
- On Day 5, embryos reach the blastocyst stage, which increases the chances of implantation.
Only the best-quality embryos are chosen for transfer, while the remaining healthy embryos may be frozen for future use (embryo cryopreservation).
Step 6: Embryo Transfer
The final step of the ICSI process is embryo transfer, where one or more embryos are placed into the uterus. This is a simple and painless procedure performed without anesthesia.
The steps of embryo transfer include:
- Loading the embryo(s) into a thin, flexible catheter.
- Gently inserting the catheter through the cervix into the uterus.
- Depositing the embryo(s) in the uterine lining.
Following the transfer, the patient is advised to rest for a short period before resuming normal activities.
Step 7: Luteal Phase and Pregnancy Test
After the embryo transfer, the luteal phase begins, where the woman takes progesterone supplements to support implantation and early pregnancy.
- A blood test for pregnancy (beta hCG test) is conducted 12-14 days after embryo transfer to confirm if implantation was successful.
- If the test is positive, the patient continues hormonal support until the placenta develops.
- If implantation does not occur, the couple can discuss further options with their infertility specialist in Lahore, including another cycle or frozen embryo transfer (FET).
Conclusion:
ICSI is a highly effective fertility treatment, particularly for couples facing male infertility issues. By injecting a single healthy sperm directly into an egg, ICSI increases fertilization rates and improves the chances of pregnancy.
If you are considering ICSI treatment, consulting an experienced infertility specialist in Lahore can help determine if this procedure is the right option for you. With advancements in reproductive medicine, couples struggling with infertility now have a greater chance of achieving their dream of parenthood.
What's Your Reaction?



















